How China Dominates the Global Battery Supply Chain
China’s dominance in the global battery supply chain is a critical factor influencing the production and availability of batteries worldwide. This article explores how China controls various stages of battery production, its impact on global markets, and emerging alternatives to reduce dependence on Chinese manufacturing.
What Is China’s Role in the Global Battery Supply Chain?
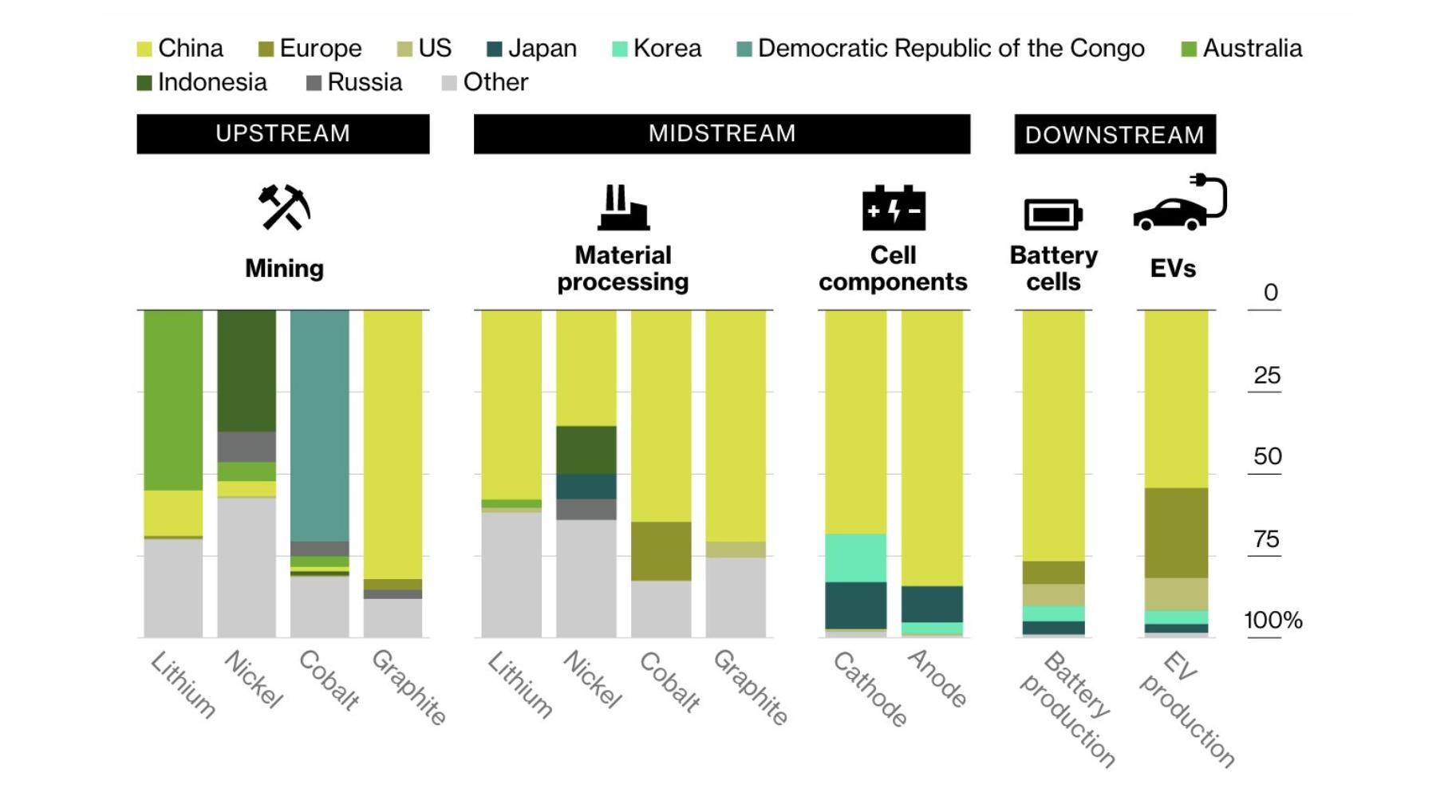
China plays a pivotal role in the global battery supply chain, controlling a significant portion of both raw material processing and battery manufacturing. The country is responsible for over 70% of global lithium-ion battery production, which is essential for electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and consumer electronics. This dominance positions China as a central player in the transition to clean energy.Chart: China’s Share in Global Battery Production
| Component | Percentage Controlled by China |
|---|---|
| Lithium Processing | 66% |
| Cobalt Processing | 80% |
| Graphite Processing | 100% |
| Final Battery Production | 80% |
How Does China Control the Mining and Processing of Battery Materials?
China’s control over the mining and processing of critical battery materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite is substantial:
- Mining Operations: While countries like Australia and the Democratic Republic of Congo hold significant mineral reserves, Chinese companies have invested heavily in mining operations abroad.
- Processing Facilities: China dominates the processing stage, refining raw materials into usable forms for battery production. For instance, it processes nearly all graphite used in batteries.
- Strategic Partnerships: Chinese firms often enter into strategic partnerships or acquire stakes in foreign mines to secure a steady supply of essential materials.
What Are the Stages of Battery Production Dominated by China?
China’s dominance spans multiple stages of battery production:
- Raw Material Extraction: Although not all raw materials are sourced from within China, it controls a large portion of processing.
- Material Processing: As mentioned, it processes most lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite.
- Manufacturing Components: The country produces almost all anodes and cathodes used in batteries.
- Final Assembly: Finally, over 80% of finished battery cells are manufactured in China.
Chart: Stages of Battery Production Dominated by China
| Stage | Percentage Controlled by China |
|---|---|
| Raw Material Extraction | Varies by mineral |
| Material Processing | Lithium: 66%, Cobalt: 80% |
| Component Manufacturing | Anodes: ~90%, Cathodes: ~70% |
| Final Assembly | ~80% |
Why Is China’s Battery Manufacturing Capacity Significant?
China’s manufacturing capacity is significant due to several factors:
- Economies of Scale: Chinese manufacturers benefit from large-scale production capabilities that reduce costs.
- Government Support: The Chinese government provides substantial subsidies and support to its battery manufacturers, enhancing competitiveness.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous investment in research and development has positioned Chinese companies at the forefront of battery technology.
How Does China’s Dominance Affect Global Prices and Supply Chains?
China’s control over the battery supply chain has profound implications for global prices and supply chains:
- Price Control: With such a large share of production, China can influence prices for key materials and components.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Countries relying heavily on Chinese batteries face risks associated with geopolitical tensions or trade disputes.
- Market Entry Barriers: New entrants to the market find it challenging to compete against established Chinese manufacturers due to cost advantages.
What Challenges Does China Face in Its Battery Supply Chain?
Despite its dominance, China faces several challenges:
- Dependence on Imports: While it leads in processing and manufacturing, it still relies on imports for many raw materials.
- Environmental Concerns: The environmental impact of mining and processing operations has drawn criticism and may lead to stricter regulations.
- Geopolitical Risks: Tensions with other countries can disrupt supply chains or lead to sanctions that affect production capabilities.
What Alternatives Are Emerging to Reduce Dependence on China?
Countries are exploring several alternatives to reduce their dependence on Chinese battery production:
- Local Sourcing Initiatives: Nations are investing in domestic mining operations for critical minerals.
- Diversifying Supply Chains: Efforts are underway to establish supply chains that do not rely solely on Chinese sources.
- Innovative Technologies: Research into alternative battery technologies (e.g., lithium-sulfur) may provide new options that lessen reliance on traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Industrial News
Recent developments highlight increasing efforts from various countries to diversify their battery supply chains away from Chinese dominance. The U.S., Canada, and European nations are investing heavily in local mining operations and refining capabilities to secure their own sources of critical minerals needed for battery production. Additionally, innovative technologies are being explored to create more sustainable alternatives that do not rely heavily on traditional lithium-ion chemistry.
LiFePO4 Battery Expert Views
China’s grip on the global battery supply chain presents both challenges and opportunities,” states Dr. Emily Chen, an expert in energy storage technologies. “While their dominance is significant, emerging markets are beginning to explore local sourcing strategies that could reshape the landscape.”
FAQ Section
- Q1: Why does China dominate the battery supply chain?
China dominates due to its extensive processing capabilities, government support, economies of scale, and technological advancements. - Q2: What are the risks associated with relying on Chinese batteries?
Risks include price fluctuations, geopolitical tensions affecting supply chains, and environmental concerns related to mining practices. - Q3: Are there alternatives to Chinese batteries?
Yes, countries are exploring local sourcing initiatives and innovative technologies like lithium-sulfur batteries to reduce dependence on traditional lithium-ion batteries produced in China.
